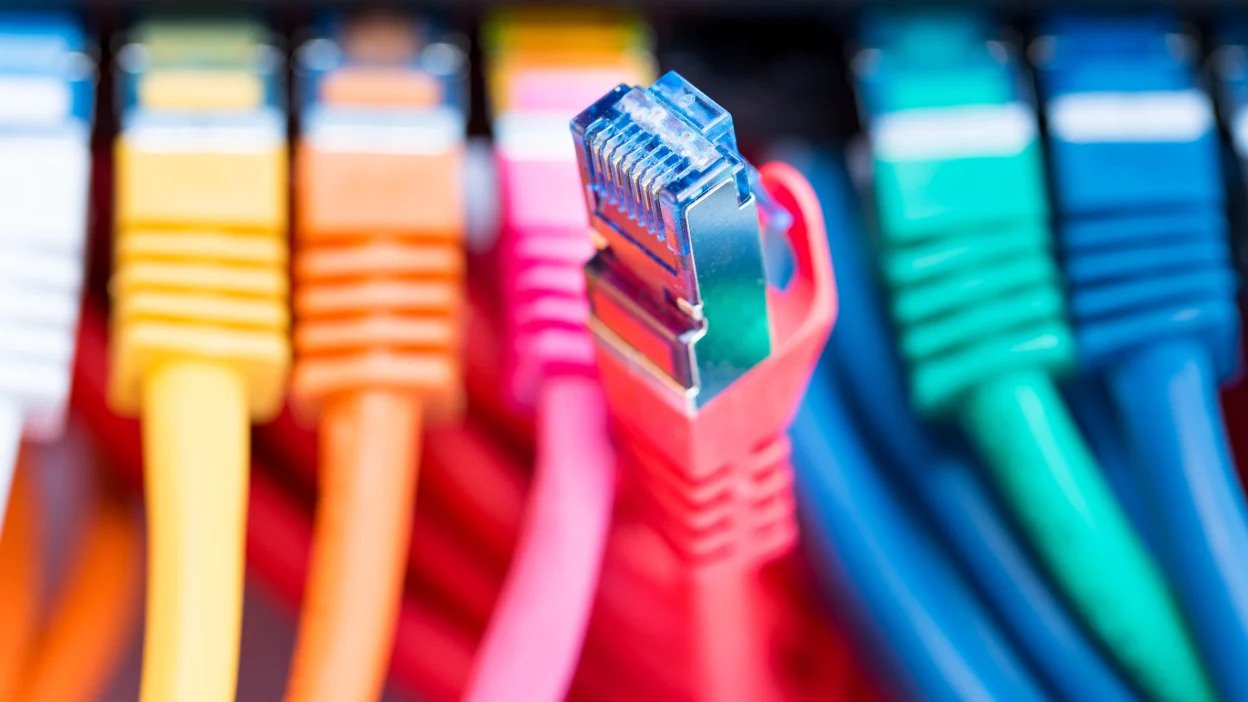
Depending upon technical specifications, there are multiple types of networking cables including Twisted Pair, Coaxial, Ethernet, and fiberoptic. Not all of these cables are interchangeable, that is they are best suited for specific purposes and each should be deployed to meet specific networking goals. Therefore, those who are interested in buying networking cables are advised to read this article before making a final investment.
Table of Content
Networking Cables:
Networking cables are used to connect computers and networking devices in a network. Networking cables are deployed to relay important data, set up servers, and operate the devices which are essential for running business applications. Cables can be used externally to plug for plugging computers into internet modems or grounded portals and they are also built into walls along with electrical wiring to provide ready access to the internet.
Types of Networking Cables:
The most popular networking cables used nowadays are of three kinds:
- Coaxial Cables
- Twisted Pair Cables
- Fiberoptic Cables
Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables are high-frequency transmission cables that comprise solid copper as an inner conductor surrounded by foam insulation, symmetrically-wrapped woven braided shield, and plastic jackets. The inner conductors carry electrical signals and the shielding designs make sure that data is transmitted rapidly without any interference from environmental factors. Some features of Coaxial cables have been discussed below:
- Coaxial cables are very resistant to signal obstruction and metal shields protect networks from outside interferences from fluorescent and EMI (Electromagnetic Interferences) and OBI (Optical Beat Interferences).
- Coaxial cables are easy to install, maintain and operate. They don’t warrant sophisticated tools, precise alignment, and other demanding infrastructure and skills. Furthermore, coaxial cables can be expanded easily and if damaged, can be repaired easily by the homeowner or network administrators without any requirement of fusion splicing or splice enclosure which are required by Fiberoptic cables.
- These networking cables are resistant enough to withstand rugged working conditions. They can resist cut-through, crushing, and bending.
- Most importantly, coaxial cables can support high-bandwidth transmission in comparison with Twisted Pair cables and perform exceptionally well for short-distance transmission.
- Downsides of coaxial cables are also many. They are bulky and less pliable which makes it hard for the network administrators to deploy them, particularly, if the coating is thick, the situation gets more complicated. The signal leakage, speed fluctuation, and inability to transmit data at longer distances are also some drawbacks. Therefore, coaxial cables are preferred by home/ home offices and by those firms that don’t require a larger network infrastructure.
Twisted Pair Cables
This is also a popular networking cable solution that is being deployed by homes and business-based Ethernet networks. Twisted Pair cables contain four pairs of insulated strands of copper wires inside the lining of the cable. Each pair is twisted further into additional twists for protection against interference from the other devices and the stoppage of electromagnetic radiation. This arrangement of twisted pairs helps increase the reliability of the network and makes sure that network failures remain minimum. Like Coaxial cables, twisted pair cables are also being used for running various applications and meeting different purposes like telephone lines, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL), and Local Area Networks.
Categories of Twisted Pair Cables:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair Cables(UTP)
- Shielded Twisted Pair Cables(STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair Cables(UTP):
UTP cables generally consist of wires and insulators but they don’t include foil or braiding as insulators, resultantly, they don’t provide much protection against crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. But, UTP has been the most popular option for Ethernet installation. They can support high data transmission rates of up to 1 Gigabit per second(Gbps). UTP cables are easy to install and troubleshoot. But one critical downside is that they cannot be deployed for long-distance data transmission. After 100m, one needs to install repeaters for carrying forward the data.
Shielded Twisted Pair Cables(STP):
STP cables are provided with aluminum foil around the conductors for improving the cables’ abilities to resist noise and signal interference. Though STP cables are expensive and difficult to scale, they provide better protection against signal interference in comparison with UTP cables. They are also used for providing grounding as well.
Categories of Twisted Pair Cables On the Basis of Speed:
Depending upon the speed and number of twists, Twisted Pair cables are divided into multiple categories abbreviated as “cat”.
-
Cat 1 and Cat 2 Cables:
These cables have maximum data rates of 1 Mbps and 4 Mbps respectively. Cat1 don’t support data transmission that’s why they were used exclusively for telephone lines. Cat 2 is used for the Token Ring network and it does not support a high transmission rate. These categories are no longer used extensively.
-
Cat 3 Cables:
Cat 3 is the network wire and is capable of 10 Mbps data up to 100m distance. Cat 3 is the minimum cable specification for 10 Base-T Ethernet, which is a local area network. Cat 3 has become obsolete and is no longer available on the market.
-
Cat 4 Cables:
This cable can support a 16 Mbps data transmission rate up to 100 m distance and it is deployed for Token Ring.
-
Cat 5 Cables:
Cat 5 cables comprise two pairs and can support 100 Mbps speed. This cable can be laid up to 100m without any data interruption. Though these cables are no longer readily available on the market, Internet Service Provider(ISP) companies use these cables for providing connection to users.
-
Cat 5 E Cables:
This cable is generally considered the best option for home-based internet where one needs to build a small network connecting a few computers and printers. This can support 1 Gbps data transmission and the laying distance is again 100m. You can also use this cable for the surveillance system as well if the requisite internet speed is 1 Gbps or below.
-
Cat 6 Cables:
Cat 6 cables are the most popular choice in the IT industry. It has 4 pairs and can support 10 Gbps speed up to 55 meters. Additionally, there is a plastic separator inside that reduces the crosstalk and minimizes the interferences. There is also a premium shielded Cat 6 option which further reduces the crosstalk and helps you transmit data without any external noise or electromagnetic interferences. Cat 6 cables are used for setting up commercial networks and gigabit Ethernet connectivity. Another variant is Cat6 A which provides the same features except enhanced capability to transmit data up to 100 meters. There are also STP and UTP options available under categories. If you are looking for concealed cable installation (inside the walls), you should go for Cat6 or Cat6 A, Cat5 category is not suitable for concealing.
-
Cat 7 Cables:
These cables are designed for meeting the requirement of 10 Gbps core infrastructure. They can support transmission up to 100 m. The four individually-shielded copper wires ensure greater protection against crosstalk and EMI. This is a premium cable solution and causes steep upfront costs for the organizations.
-
Cat 8 Cables:
Cat 8 cables are the fastest Ethernet cables ever so far. They can support up to 40 Gbps speed, four times faster than cat6 cables. This is the most expensive cabling solution and it is deployed for high-end switch-to-switch communication in 25 Gbps and 40 Gbps networks. Cat 8 cables are capable of completely eliminating crosstalk and other interferences.
Fiberoptic Cables:
Fiberoptic cables comprise extra-thin crystal of glass and their protective covering. Fiberoptic cables have been designed to transmit data over long distances without any need for repeaters to boost the signals. Unlike Coaxial and Twisted Pair cables that transmit data in the form of signals within insulated copper wires, Fiberoptic cables transmit data in the form of pulses. They provide some distinct advantages:
- Fiberoptic cables don’t leak signals and they are prone to EMI (Electromagnetic Interference);
- They can support higher bandwidth and can transmit data up to 2km without repeaters. Hence, there is no attenuation problem, which makes them highly suitable for Wide Area Networks(WAN) or office uses where there is a huge volume of communication traffic;
- The downside is the steep price and requirement of skilled IT staff for their installation which further adds to the overall cost.
Some Quick Words About Morgan Ingland LLC:
Morgan Ingland LLC specializes in supplying cost-effective cabling hardware along with accessories like faceplates, Cable Ties, Cable Organizers, etc. Every kind of Ethernet cable/networking cable including but not restricted to coaxial cables, Fiberoptic cables, firewall cables, and signal cables, among others, are available at our stores at the most competitive price in the market. Feel free to contact us at 415-704-8713 or email us at info@miatlantic.us 24/7 for further detail and information. We are ready to serve you 24/7.
 Live-Chat
Live-Chat